- Help Center
- Machine Learning
- Supervised
-
Data Science Bootcamp
-
Large Language Models Bootcamp
-
Agentic AI Bootcamp
-
Registration
-
Pricing
-
Community
-
Python Programming
-
Platform Related Issues
-
Bootcamps
-
Homework and Notebooks
-
Free Courses
-
Data Science for Business
-
Practicum
-
Blog
-
Employment Assistance
-
Machine Learning
-
Data Analysis
-
R Language
-
Python for Data Science
-
SQL
-
Introduction to Power BI
-
Power BI
-
Programming and Tools
-
Partnerships
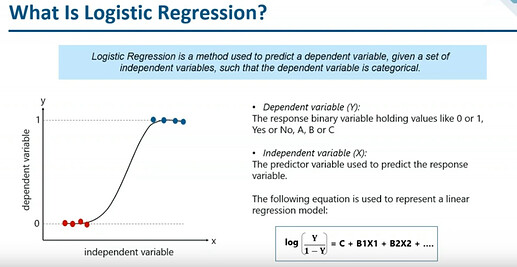
What Is Logistic Regression?
Logistic regression is a supervised machine learning algorithm that accomplishes binary classification tasks by predicting the probability of an outcome, event, or observation.
The model delivers a binary or dichotomous outcome limited to two possible outcomes: yes/no, 0/1, or true/false.
A logistic function known as the sigmoid function is used in logistic regression to map predictions and their probability. An S-shaped curve known as the sigmoid function transforms any real value into a range between 0 and 1.
Additionally, the model predicts that the output belongs to that class if the sigmoid function’s output (estimated probability) is higher than a predetermined threshold on the graph. The model predicts that the output does not belong to the class if the estimated probability is less than the threshold.